|
Advertisement / Annons: |
Debris finder, PolCor-2
|
Content:
|
17: Test of the instrument that has been done
Göran tells: "One thing that must be handled is the background light (light pollution and the noise from this). One method that is common in the IR wavelength is to move the image field (chopping and / or node) to the side where no object are and take a new image. This image is then subtracted from the object image. Proven technology, but more than half of the exposure time is lost in the overhead. The optical chopper carrying out this is not on the pictures we've seen here. Tests show that the instrument PSF (Point Spread Function) behaves well and the instrument is well suited for high contrast imaging."
The test that has been performed including the red halo surrounding a compact blue galaxy and verified, object Mrk900. Simply put, the focused image is well composed. In this test the camera's gain is set to 100, and 12,000 images were collected respectively. Of these 85% were used in the final image. The frame rate was set to 10 Hz. To read the full report there is a link at the end where it can be downloaded as a PDF file, written in English. 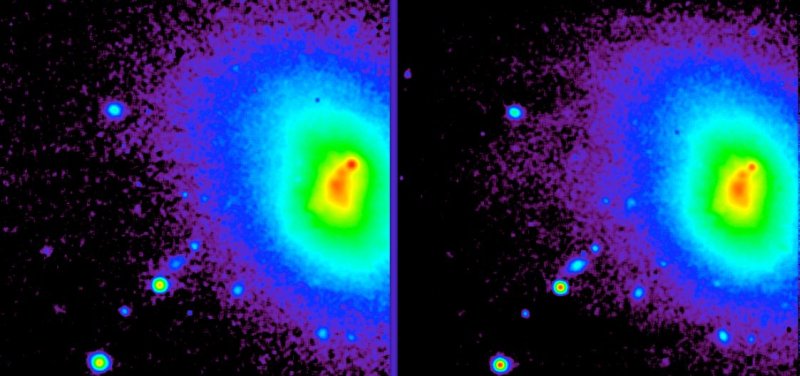
Mrk900 in Visual filter (left) and Infrared filter (right). The instrument has also been used successfully to detect AGB envelops (stars to become planetary nebulas), and more normal high-resolution images without the pole filter and the coronagraph mask that normally sits in the path. The instrument, however, is in an early phase and still has no measurements made on young stars and the dust ring that was written about in the beginning of this article. Watch NOT's website if something comes up there in future.
|
|